What Is ERP?
ERP stands for enterprise resource planning.
An ERP system is an integrated platform for managing large amounts of data in the production and supply chains. The system is divided into numerous modules that handle finance, accounting, procurement, human resources, manufacturing and delivery, which allows businesses to encompass and automate all processes.
ERP Benefits and Drawbacks
As treatments become increasingly automated, Health IT is expanding.
What is the main driver for the growth of this market? Simply put, it’s the desire of organizations to increase their process transparency and operational efficiency.
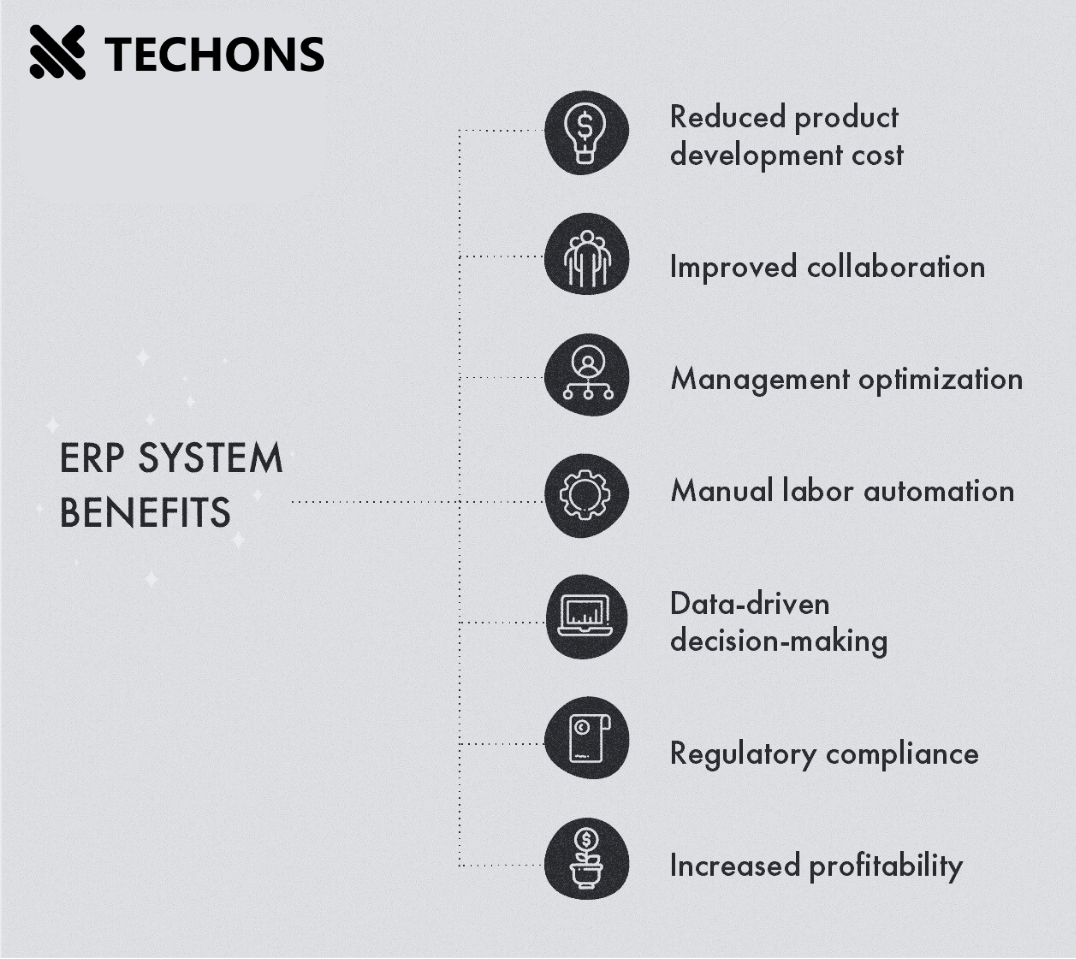
The ERP system implementation requires a considerable amount of time, financial expenses and the engagement of all departments within the company. Such enormous effort to create the right enterprise resource planning solution pays off with numerous benefits:
-
Reduced product development cost — effective management and quality assurance systems minimize errors and risks.
-
Improved collaboration — information barriers between departments are eliminated as there is a single database.
-
Management optimization — all processes are controlled via a single center, so no issue can be missed.
-
Manual labor automation — smart digital technologies incorporated into ERPs replace humans in many operations.
-
Data-driven decision-making — real-time data analysis allows managers to make decisions quicker.
-
Regulatory compliance — specialized automated systems are taught to monitor compliance of produced goods with relevant rules and standards.
-
Increased profitability — the above-mentioned benefits together provide full enterprise visibility and efficient operations, helping reach the common goal of enhancing the output.
There are a few drawbacks that come with the migration to enterprise resource planning:
-
The high cost of implementation and maintenance (the more modules are needed, the more expensive the system is)
-
A complicated integration process that requires a compatible business environment and full engagement of all the teams
ERP’s Interior
Typically, enterprise resource management software has a modular architecture, meaning that workers can access only those modules of the system that concern their duties, while top management can both review data and make changes within the entire system. By keeping to a modular approach, companies enhance security and get more accurate data at all levels.
Functionality
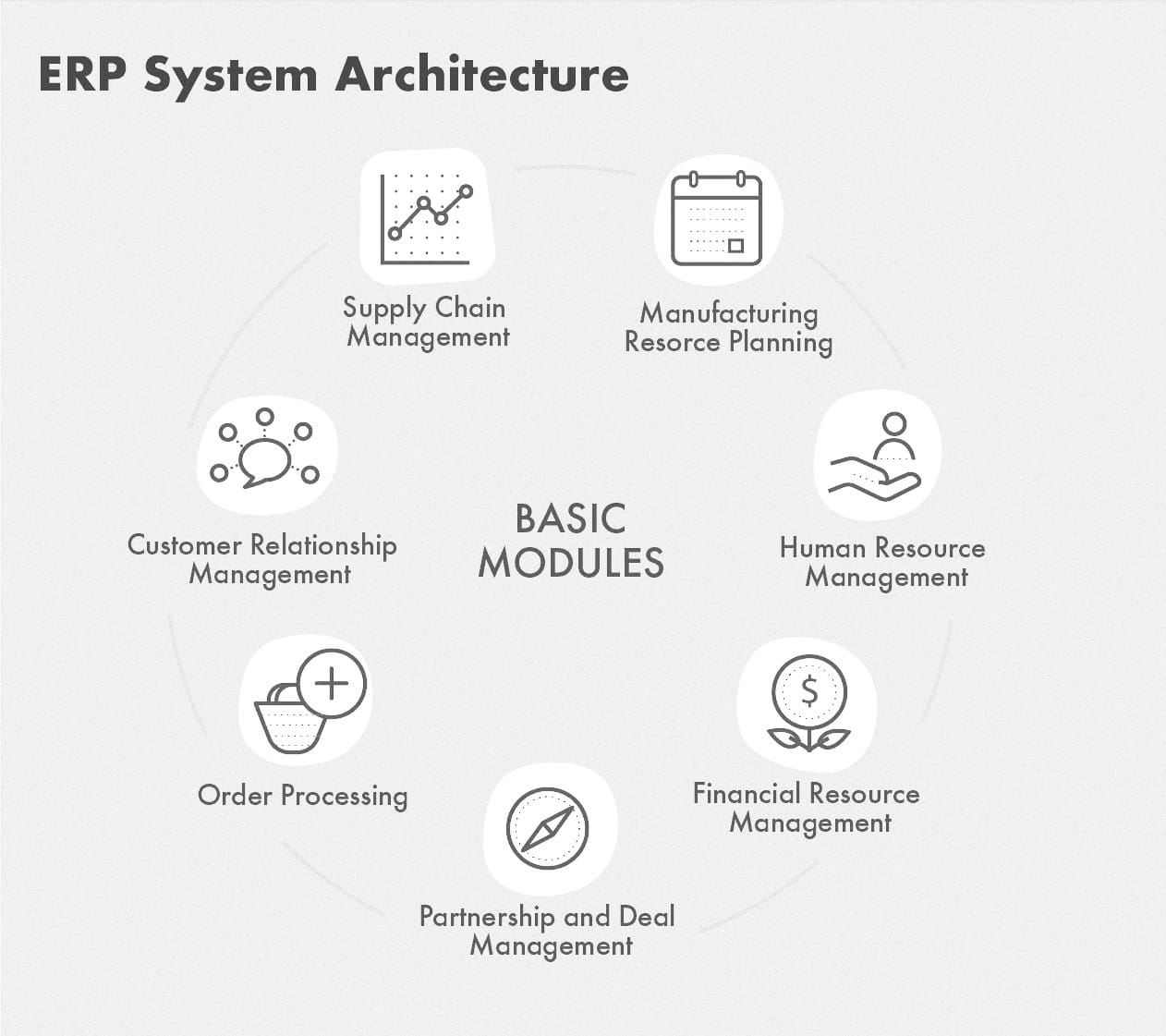
In general, ERP modules perform the following functionality — all from the single platform:
-
Order processing
-
Production management and manufacturing resource tracking
-
Supply chain management
-
Customer relation management
-
Content management
-
Human resources management
-
Partnership and deal management
-
Financial management
-
Marketing
Developing a Custom ERP: Step by Step
An ERP system is an integrated platform for managing large amounts of data in the production and supply chains. The system is divided into numerous modules that handle finance, accounting, procurement, human resources, manufacturing and delivery, which allows businesses to encompass and automate all processes.
What is the main driver for the growth of this market? Simply put, it’s the desire of organizations to increase their process transparency and operational efficiency.
The ERP system implementation requires a considerable amount of time, financial expenses and the engagement of all departments within the company. Such enormous effort to create the right enterprise resource planning solution pays off with numerous benefits:
- Reduced product development cost — effective management and quality assurance systems minimize errors and risks.
- Improved collaboration — information barriers between departments are eliminated as there is a single database.
- Management optimization — all processes are controlled via a single center, so no issue can be missed.
- Manual labor automation — smart digital technologies incorporated into ERPs replace humans in many operations.
- Data-driven decision-making — real-time data analysis allows managers to make decisions quicker.
- Regulatory compliance — specialized automated systems are taught to monitor compliance of produced goods with relevant rules and standards.
- Increased profitability — the above-mentioned benefits together provide full enterprise visibility and efficient operations, helping reach the common goal of enhancing the output.
There are a few drawbacks that come with the migration to enterprise resource planning:
- The high cost of implementation and maintenance (the more modules are needed, the more expensive the system is)
- A complicated integration process that requires a compatible business environment and full engagement of all the teams
Typically, enterprise resource management software has a modular architecture, meaning that workers can access only those modules of the system that concern their duties, while top management can both review data and make changes within the entire system. By keeping to a modular approach, companies enhance security and get more accurate data at all levels.
In general, ERP modules perform the following functionality — all from the single platform:
- Order processing
- Production management and manufacturing resource tracking
- Supply chain management
- Customer relation management
- Content management
- Human resources management
- Partnership and deal management
- Financial management
- Marketing